Emergency Generators: Essential Backup Power Solutions for Your Home
Power outages can strike at any time, leaving homes vulnerable to disruptions in essential services, food spoilage, and even safety concerns. As extreme weather events become more common and electrical grid demands increase, emergency generators have evolved from luxury items to practical necessities for many homeowners. These backup power systems provide electricity when utility power fails, ensuring continuity for critical home functions and peace of mind during outages.
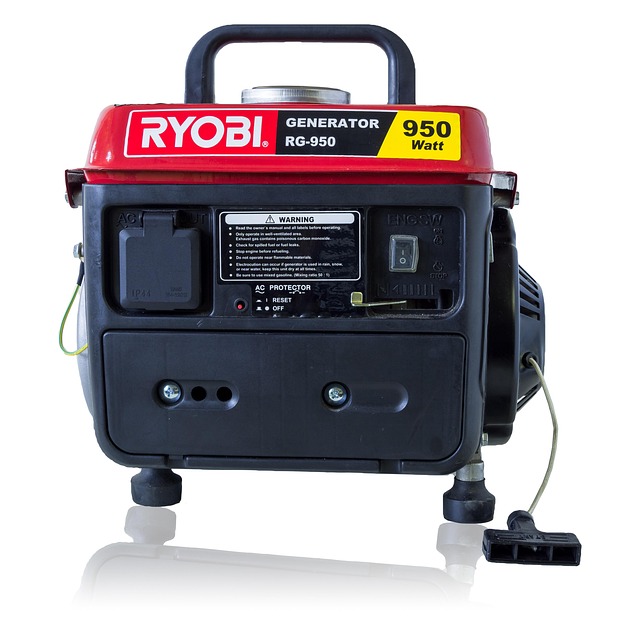

Home Power Generators: Essential Backup for Modern Living
Today’s homes rely heavily on electricity to power everything from refrigerators and heating systems to medical equipment and home offices. When the power grid fails, even briefly, the consequences can range from inconvenient to dangerous. Emergency generators serve as a crucial safety net, automatically detecting outages and supplying backup power within seconds.
Modern living demands consistent electricity for maintaining food safety, climate control, security systems, and communication devices. For families with young children, elderly members, or individuals with medical needs that require powered equipment, a reliable backup power source isn’t merely convenient—it’s essential. Additionally, with more people working remotely, power continuity has become critical for professional obligations and economic stability.
Understanding Home Generator Types: Standby, Portable & Inverter
Home generators generally fall into three main categories, each serving different needs and budgets:
Standby Generators are permanent installations connected directly to your home’s electrical system and natural gas line or propane tank. These units automatically detect power outages and start providing electricity within seconds, without requiring manual intervention. Ranging from 7kW to 38kW for residential use, they can power entire homes or selected circuits depending on capacity. Though offering the most comprehensive protection, they require professional installation and represent the highest investment.
Portable Generators provide flexibility and lower initial costs. These gas, propane, or diesel-powered units can be moved where needed and typically deliver 3kW to 10kW of power. They require manual startup and extension cords to connect appliances directly, though transfer switches can be installed for more convenient operation. While more affordable and versatile, they offer less capacity and convenience than standby models.
Inverter Generators represent newer technology that converts AC power to DC, then back to clean AC power. This results in more stable electricity that’s safe for sensitive electronics. They’re typically more fuel-efficient, quieter, and lighter than traditional portable generators, though they generally provide less power (1kW to 7kW) and come at premium prices for their size.
How to Select the Right Home Backup Generator for Your Needs
Choosing an appropriate emergency generator requires careful consideration of several factors:
-
Power Requirements: Calculate the total wattage needed by listing essential appliances and their starting (surge) and running wattage. Common necessities include refrigerators (700-1,200 watts running), sump pumps (800-1,500 watts), heating systems (500-1,500 watts), and lighting (60-600 watts depending on type and quantity).
-
Fuel Type: Consider availability, storage requirements, and runtime. Natural gas offers convenience for standby generators but requires existing lines. Propane burns cleaner than gasoline and stores indefinitely. Gasoline is readily available but has storage limitations and shelf-life concerns.
-
Installation Location: Generators produce carbon monoxide and require proper ventilation. Standby units must be installed outdoors with appropriate clearance from windows and doors. Even portable generators must operate at least 20 feet from the home with exhaust directed away from structures.
-
Runtime and Fuel Efficiency: Consider how long the generator can run on a full tank or continuous fuel source. This is particularly important during extended outages when refueling options may be limited.
-
Noise Level: Generator noise can range from conversational level (50-60 dB) for premium inverter models to lawn mower volume (80-95 dB) for standard portable units. Consider neighborhood regulations and personal tolerance.
Professional Generator Installation: Ensuring Safety & Reliability
Professional installation is mandatory for standby generators and highly recommended for transfer switches used with portable models. Improper installation can lead to dangerous situations including:
-
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Proper placement and venting prevent exhaust gases from entering living spaces.
-
Electrical Hazards: Professional installation ensures appropriate circuit protection, grounding, and connection to the home’s electrical panel.
-
Improper Fuel Line Connections: Gas line installations require licensed professionals to prevent leaks and ensure compliance with local codes.
-
Backfeeding: Without proper transfer switches, generators can send electricity back through utility lines, endangering utility workers—a situation professionals prevent through proper equipment installation.
Professional installation also typically includes obtaining necessary permits, coordinating with utility companies, performing load calculations, and ensuring compliance with local building codes and manufacturers’ specifications. While adding to upfront costs, professional installation ensures safety, reliability, and often preserves warranty coverage.
Home Standby Generator Costs: Equipment, Installation & More
Home generator systems represent a significant investment that varies substantially based on type, capacity, and installation requirements.
| Generator Type | Average Equipment Cost | Typical Installation Cost | Total Investment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable (5-8kW) | $500-$1,500 | $300-$500 (transfer switch) | $800-$2,000 |
| Inverter (2-5kW) | $1,000-$4,000 | $300-$500 (transfer switch) | $1,300-$4,500 |
| Small Standby (8-12kW) | $2,500-$4,500 | $1,000-$3,000 | $3,500-$7,500 |
| Medium Standby (13-20kW) | $3,500-$6,000 | $1,500-$3,500 | $5,000-$9,500 |
| Large Standby (21-38kW) | $5,000-$15,000 | $2,000-$5,000 | $7,000-$20,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Beyond the initial purchase and installation, ongoing costs include:
-
Maintenance: Annual service ($200-$500) to check electrical connections, change oil and filters, and test functionality
-
Fuel costs: Natural gas ($20-$60/month for standby systems during normal testing)
-
Repairs: Occasional part replacements ($150-$1,000 depending on components)
-
Permit fees: Typically $50-$200 depending on locality
While these costs are substantial, many homeowners find the investment worthwhile when considering potential losses from extended power outages, including food spoilage, frozen pipe damage, basement flooding, business interruption, and hotel expenses during uninhabitable conditions.
Conclusion
Emergency generators provide critical protection against increasingly common power disruptions, offering peace of mind and practical benefits for modern homes. Understanding the differences between standby, portable, and inverter generators helps homeowners select appropriate systems based on their power needs, budget, and installation considerations. While representing a significant investment, properly installed and maintained generators deliver reliable backup power that protects both property and quality of life during outages.